
This poisoning is most often associated with infections by computer viruses, malware or network attacks that put in invalid DNS entries within the cache database. What is DNS cache poisoning?Ī DNS cache is polluted or poisoned when you have unauthorized domain names or IPs being inserted into it. You can flush DNS cache at different levels. This ensures that the DNS lookup process doesn’t start afresh. What this means is that if the local DNS database or DNS cache is empty, it is possible that the resolver has a cached copy of the same information. In each of these steps, there is information that is gathered and then cached or stored for later reference or use. In a new DNS lookup, the process involves checking in the resolver, the root server, and the TLD server. DNS caching doesn’t only happen at the browser and operating system levels. In the DNS cache database, there is a list comprising all domain names you have visited in the recent past and the addresses that DNS allocated them when you first made a request. When accessing a website using its URL or domain name, your computer first tries to look up their IP addresses within the DNS cache database before the browser issues the request to your router. In the same way you have a phone number for each person in your contact list, the DNS cache on your computer holds the number corresponding to each website you visit. Once you put the phone number in your contact list, you never have to ask your friend for that person’s phone number again. It’s like asking your friend for someone’s phone number.
This can happen when the server cannot identify the IP address that it allocated to the website and sends to your device. When you looked at the problem, there was nothing wrong with the internet connection, and upon visiting other sites, you got the same error message. You have likely encountered a “time-out” or “DNS server cannot be reached” error message when trying to visit a site that you previously visited. When you access a domain name for the first time, your computer does a DNS request to a server.
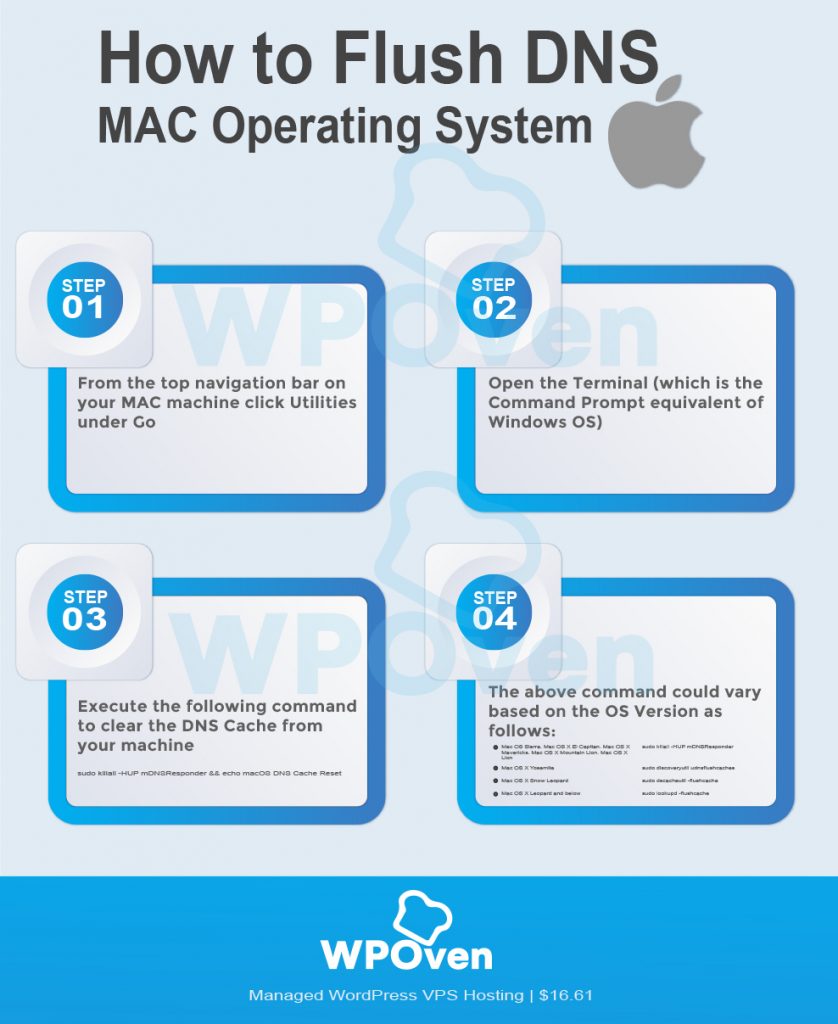
#OSX FLUSH DNS HOW TO#
When looking at how to flush DNS, it is important to know what is DNS cache.

Sounds good, right? But there are times when you will want to flush your DNS cache and remove this trail.ĭNS is essentially the internet directory. A Domain Name System (DNS) cache remembers the websites you visit so you can load them faster in the future.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
